防静电塑料橡胶制品表面电阻率测定仪 本仪器既可测量高电阻,又可测微电流。采用了美国Intel公司的大规模集成电路,使仪器体积小、重量轻、准确度高。以双3.1/2位数字直接显示电阻的高阻计和电流。量限从1?104Ω ~1?1018Ω,是目前国内测量范围 宽,准确度 高的数字超高阻测量仪。电流测量范围为2?10-4~1?10-16A。机内测试电压为10/50/100/250/500/1000V任意可调。本仪器具有精度高、显示迅速、性好稳定、读数方便, 适用于防静电产品如防静电鞋、防静电塑料橡胶制品、计算机房防静电活动地板等电阻值的检验以及绝缘材料和电子电器产品的绝缘电阻测量。本仪器除能测电阻外,还能直接测量微弱电流。
This instrument can measure both high resistance and micro current. Adopting large-scale integrated circuits from Intel Corporation in the United States, the instrument has a small size, light weight, and high accuracy. A high resistance meter that displays resistance and current directly using double 3.1/2 digits. The measurement limit ranges from 1?104Ωto 1?1018Ω, making it a widely used and highly accurate digital ultra-high resistance measuring instrument in China. The current measurement range is 2?10-4 to 1?10-16A. The test voltage inside the machine can be adjusted to any of 10/50/100/250/500/1000V. This instrument has high accuracy, fast display, good stability, and convenient reading. It is suitable for testing the resistance values of anti-static products such as anti-static shoes, anti-static plastic and rubber products, anti-static raised floors in computer rooms, as well as measuring the insulation resistance of insulation materials and electronic and electrical products. This instrument can not only measure resistance, but also directly measure weak currents.
防静电塑料橡胶制品表面电阻率测定仪 典型应用
1.测量防静电鞋、导电鞋的电阻值
2、测量防静电材料的电阻及电阻率
3、测量计算机房用活动地板的系统电阻值
4、测量绝缘材料电阻(率)
5、光电二极管暗电流测量
6、物理,光学和材料研究
Typical applications
1. Measure the resistance value of anti-static shoes and conductive shoes
2. Measure the resistance and resistivity of anti-static materials
3. Measure the system resistance value of the raised floor used in the computer room
4. Measure the resistance (rate) of insulation materials
5. Measurement of Dark Current in Photodiodes
6. Physics, Optics, and Materials Research
电源
要求有很稳定的直流电压源。这可用蓄电油或一个整流稳压的电摞来提供。对电源的稳定度要求是由电压变化导致的电流变化与被测电流相比可忽略不计。
加到整个试样上的试验电压通常规定为100V、250V、500V、1000 V、2500 V、5000 V, 10000 V和15000 V。 常用的电压是100V、500V和1000 V。
在某些情况下,试样的电阻与施加电压的极性有关
如果电阻是与极性有关的,则宜加以注明。取两次电阻值的几何平均值(对数算术平均值的反对数)作为结果。
由于试样电阻可能与电压有依存关系,因此应在报告中注明试验电压值。
Power Supply
Require a very stable DC voltage source. This can be provided by storing oil or a rectifier stabilized stack of electricity. The stability requirement for the power supply is that the current variation caused by voltage changes can be ignored compared to the measured current.
The test voltage applied to the entire sample is usually specified as 100V, 250V, 500V, 1000V, 2500V, and 5000V, 10000 V and 15000 V. The commonly used voltages are 100V, 500V, and 1000V.
In some cases, the resistance of the sample is related to the polarity of the applied voltage
If the resistance is polarity dependent, it should be noted. Take the geometric mean of two resistance values (the inverse of the logarithmic arithmetic mean) as the result.
Due to the possible dependence of sample resistance on voltage, the test voltage value should be indicated in the report.
标准配置:
1,测试仪器:1台
2,电源线:1条
3,测量线:3根(屏蔽线,测试接线,接地线)
4,使用说明书:1份
Standard configuration:
1. Testing instrument: 1 unit
2. Power cord: 1
3. Measurement wires: 3 wires (shielded wire, test wire, grounding wire)
4. User manual: 1 copy
测试电压(V)
DC—10V
DC—50V
DC—100V
DC—500V
DC—1000V
方法
测量高电阻常用的方法是直接法或比较法。
直接法是测量加在试样上的直流电压和流过它的电流(伏安法)而求得未知电阻。
比较法是确定电桥线路中试样未知电阻与电阻器已知电阻之间的比值,或是在固定电压下比较通过这两种电阻的电流。
附录A给出了描述这些原理的例子。
伏安法需要一适当精度的伏特表,但该方法的灵敏度和度主要取决于电流测量装置的性能,该装置可以是一个检流计或电子放大器或静电计。
电桥法只需要一灵敏的电流检测器作为零点指示器,测量度主要取决于已知的桥臂电阻器,这些桥臂电阻应在宽的电阻值范围内具有高的精密度和稳定性。
电流比较法的度取决于已知电阻器的度和电流测量装置,包括与它相连的测量电阻器的稳定度和线性度。只要电压是恒定的,电流的确切数值并不重要。
对于不大于1011Ω的电阻,可以按照11.1用检流计采用伏特计一安培计法来测定其体积电阻率。 对于较高的电阻,则推荐使用直流放大器或静电计。
在电桥法中,不可能直接测量短路试样中的电流(见11.1)。
利用电流测量装置的方法可以自动记录电流,以简化稳态测试过程(见11.1)。
现己有测量高电阻的一些专门的线路和仪器。只要它们有足够的度和稳定度,且在需要时能使试样短路并在电化前测量电流者,均可使用。
method
The commonly used methods for measuring high resistance are direct method or comparative method.
The direct method is to measure the DC voltage applied to the sample and the current flowing through it (volt ampere method) to obtain the unknown resistance.
The comparative method is to determine the ratio between the unknown resistance of the sample in the bridge circuit and the known resistance of the resistor, or to compare the current passing through these two resistors at a fixed voltage.
Appendix A provides examples to describe these principles.
The volt ampere method requires a voltmeter of appropriate accuracy, but the sensitivity and accuracy of this method mainly depend on the performance of the current measuring device, which can be a galvanometer, electronic amplifier, or electrostatic meter.
The bridge method only requires a sensitive current detector as a zero point indicator, and the measurement accuracy mainly depends on the known bridge arm resistors, which should have high precision and stability over a wide range of resistance values.
The degree of current comparison method depends on the known degree of the resistor and the current measuring device, including the stability and linearity of the measuring resistor connected to it. As long as the voltage is constant, the exact value of the current is not important.
For resistors not exceeding 1011Ω, the volume resistivity can be measured using a voltmeter ammeter method according to 11.1. For higher resistance, it is recommended to use a DC amplifier or an electrostatic meter.
In the bridge method, it is not possible to directly measure the current in the short-circuit specimen (see 11.1).
The method of using a current measuring device can automatically record the current to simplify the steady-state testing process (see 11.1).
There are now some specialized circuits and instruments for measuring high resistance. As long as they have sufficient degree and stability, and can short-circuit the sample and measure the current before electrification when needed, they can be used.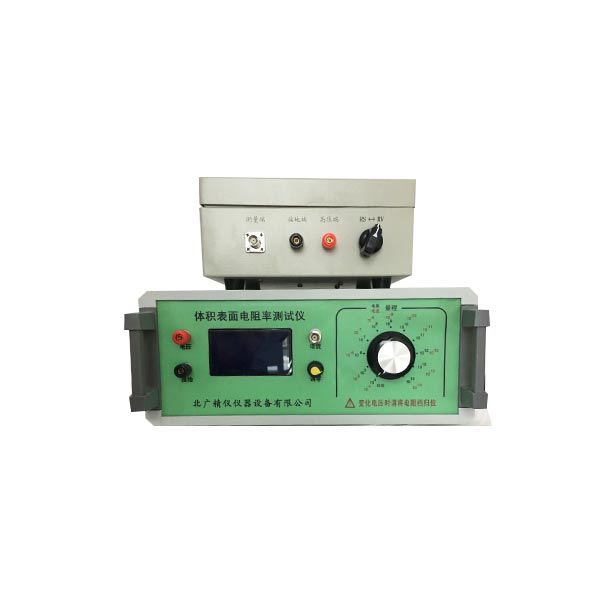
表面电阻surface resistance
在试样的其表面上的两电极间所加电压与在规定的电化时间里流过两电极间的电流之商,在两电
极上可能形成的极化忽略不计。
注1:除 非 另 有 规 定 ,表 面 电 阻 是 在 电 化 一 分 钟 后 测 定
注2通常电流主要流过试样的一个表面层,但也包括流过试样体积内的成分
报告
报告应至少包括下述情况:
a)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)关于材料的说明和标志(名称、等级、颜色、制造商等);
b)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)试样的形状和尺寸;
c)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)电极和保护装置的形式、材料和尺寸;
d)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)试样的处理(清洁、预干燥、处理时间、湿度和温度)等;
e)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)试验条件(试样温度、相对由度);
f)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)测量方法;
g)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)施加电压;
h)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)体和、电阻率(需要时);
注1:当规定了一个固定的电化时间时,注明此时间,给出个别值,并报告中值作为体积电阻率。
注2: 当在不同的电化时间后测试时,应按如下要求报告:
当在相同的电化时间里试样达到一个稳定状态肘,给出个别值,并报告中值作为体积电阻率。在这个电化时间里有某些试样不能达到稳定状态,则报告不能达到稳定状态的试样数,并分别地给出它们的结果。当测试结果取决于电化时间时,则报告它们之间的关系,例如.以图的形式或给出在电化Imin、10min和100min后的体积电阻率的中值。
i)表面电阻率(需要时):
给出电化时间为1 min的个别值,并报告其中值作为表面电阻率。
report
The report should include at least the following information:
a) Description and marking of materials (name, grade, color, manufacturer, etc.) for resistivity tester (resistivity tester);
b) The shape and size of the sample of the resistivity tester (resistivity tester);
c) The form, material, and size of electrodes and protective devices for resistivity testers (resistivity meters);
d) Processing of resistivity tester (resistivity tester) samples (cleaning, pre drying, processing time, humidity, and temperature), etc;
e) Test conditions for resistivity tester (resistivity tester) (sample temperature, relative humidity);
f) Measurement method of resistivity tester (resistivity measuring instrument);
g) Apply voltage to the resistivity tester;
h) Electrical resistivity tester (resistivity tester) body and resistivity (when needed);
Note 1: When a fixed electrification time is specified, indicate this time, provide individual values, and report the median as the volume resistivity.
Note 2: When testing after different electrification times, the following requirements should be reported:
When the sample reaches a stable state elbow within the same electrochemical time, provide individual values and report the median as the volume resistivity. If some samples cannot reach a stable state during this electrification time, report the number of samples that cannot reach a stable state and provide their results separately. When the test results depend on the electrification time, report the relationship between them, for example, in the form of a graph or provide the median volume resistivity after electrification for Imin, 10min, and 100min.
i) Surface resistivity (when needed):
Provide individual values with an electrochemical time of 1 minute and report the value as the surface resistivity.
影响电阻率的外界因素
电阻率不仅与材料种类有关,而且还与温度、压力和磁场等外界因素有关。金属材料在温度不高时,ρ与温度t(℃)的关系是ρt=ρ0(1 at),式中ρt与ρ0分别是t℃和0℃时的电阻率;α是电阻率的温度系数,与材料有关。锰铜的α约为1?10-1/℃(其数值极小),用其制成的电阻器的电阻值在常温范围下随温度变化极小,适合于作标准电阻。已知材料的ρ值随温度而变化的规律后,可制成电阻式温度计来测量温度。半导体材料的α一般是负值且有较大的量值。制成的电阻式温度计具有较高的灵敏度。有些金属(如Nb和Pb)或它们的化合物,当温度降到几K或十几K(绝对温度)时,ρ突然减少到接近零,出现超导现象,超导材料有广泛的应用前景。利用材料的ρ随磁场或所受应力而改变的性质,可制成磁敏电阻或电阻应变片,分别被用来测量磁场或物体所受到的机械应力,在工程上获得广泛应用。
电阻定律
导体的电阻R跟它的长度L、电阻率ρ成正比,跟它的横截面积S成反比,这个规律就叫电阻定律(law of resistance),公式为R=ρL/S。其中ρ:制成电阻的材料的电阻率,L:绕制成电阻的导线长度,S:绕制成电阻的导线横截面积,R:电阻值。
公式:R=ρL/S,R=U/I
ρ——制成电阻的材料电阻率,国际单位制为欧姆 ? 米(Ω ?m);
L——绕制成电阻的导线长度,国际单位制为米(m);
S——绕制成电阻的导线横截面积,国际单位制为平方米(m2) ;
R——电阻值,国际单位制为欧姆,简称欧(Ω);
U——电压值,国际单位制为伏特,简称伏(v);
I——电流值,国际单位制为安培,简称安(A)。
其中:
ρ叫电阻率:某种材料制成的长1米、横截面积是1平方毫米的导线的电阻,叫做这种材料的电阻率。是描述材料性质的物理量。国际单位制中,电阻率的单位是欧姆?米,常用单位是欧姆?平方毫米/米。与导体长度L,横截面积S无关,只与物体的材料和温度有关,有些材料的电阻率随着温度的升高而增大,有些反之。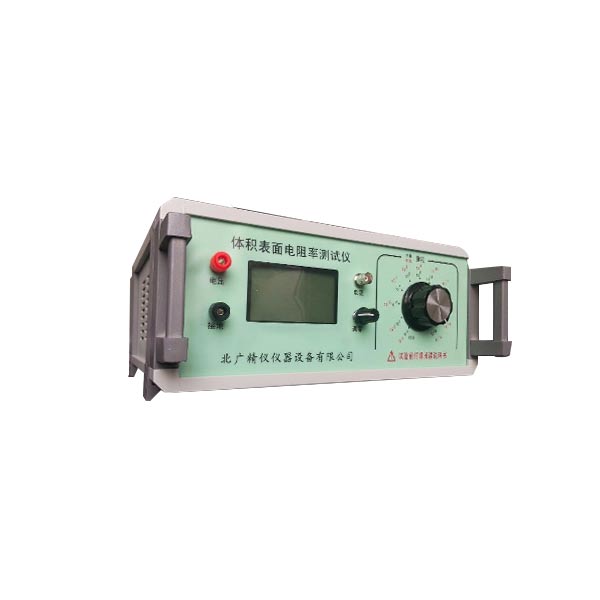
Law of resistance
The resistance R of a conductor is directly proportional to its length L and resistivityρ, and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area S. This law is called the law of resistance, and the formula is R=ρL/S. Whereρ: the resistivity of the material used to make the resistor, L:The length of the wire wound into a resistor, S:The cross-sectional area of the wire wound into a resistor, R:Resistance value.
Formula: R=ρL/S,R=U/I
ρ- the resistivity of the material used to make the resistor, measured in ohms meters (Ω?m) in the International System of Units;
L - the length of the wire wound into a resistor, measured in meters (m) in the International System of Units;
S - cross-sectional area of the wire wound into a resistor, measured in square meters (m2) in the International System of Units;
R - resistance value, expressed in ohms in the International System of Units, abbreviated as ohms (Ω);
U - voltage value, expressed in volts in the International System of Units, abbreviated as volts (v);
I - Current value, expressed in Ampere (A) in the International System of Units.
Among them:
ρis called resistivity: The resistance of a wire made of a certain material that is 1 meter long and has a cross-sectional area of 1 square millimeter is called the resistivity of this material. It is a physical quantity that describes the properties of materials. In the International System of Units, the unit of electrical resistivity is ohms per meter, and the commonly used unit is ohms per square millimeter per meter. It is not related to the length L and cross-sectional area S of the conductor, but only to the material and temperature of the object. The resistivity of some materials increases with increasing temperature, while others do not.
公司承诺:
1.购机前,我们专门派技术人员为您设计的流程和方案
2.购机后,将免费指派技术人员为您调试安装
3.整机保修一年,产品终身维护
4.常年供应设备的易损件及耗品确保仪器能长期使用
5、售后管理:我公司实现计算机化管理,实行客户定期电话回访制度,定期复查设备的工作情况,定期电话指导用户对设备进行保养和检测,以便设备正常运转,跟踪客户的设备使用情况,以便及时对设备进行维护
6、物流情况:及时提供货源,确保全国范围内2-10内到货,持续稳定地为代理商做全面服务工作,提供合理的运作空间。公司有专业的技术人员为您安装指导。
7、软件升级:终生免费提供新版本控制软件。
8、安装培训:仪器包装内附有说明书,专业培训人员为客户指定操作者讲解仪器正常操作流程、操作注意事项及仪器的日常维护要求;也可以根据客户要求提供上门培训服务。
业务咨询:932174181 媒体合作:2279387437 24小时服务热线:15136468001 盘古机械网 - 全面、科学的机械行业免费发布信息网站 Copyright 2017 PGJXO.COM 豫ICP备12019803号