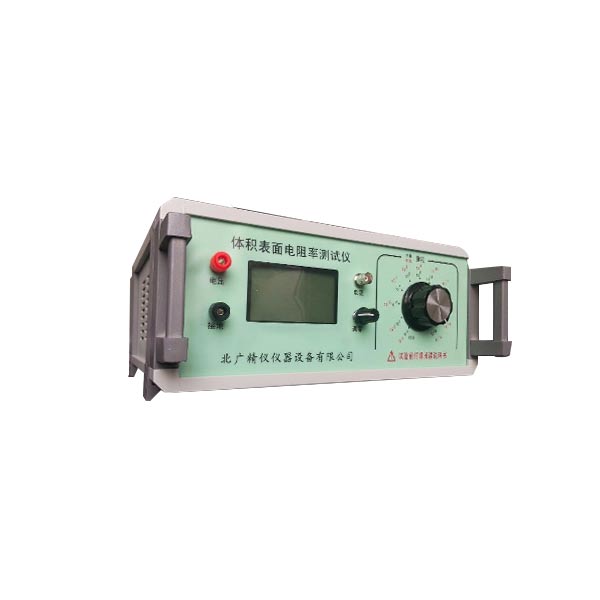
材料电阻率测试仪厂家直销 电阻的作用:
电阻在电路中的作用:利用著名的欧姆定律可以利用电阻控制电路中的电压、电流。
电阻的主要物理特征就是可以变电能为热能,因此热水器中的发热元件、电灯泡、电烫斗就是利用了电阻的作用制成的。另外电阻有怕热的特性,当导体材料温度升高时材料的电阻率会增大(有些材料则表现为减小),因此利用电阻的这种特性可以制作温度测量计(不知道你看见过没,插一根“铁丝”就能测量温度的方法就是利用了这种电阻材料作用的)。
另外一些材料的电阻还会受到光线照射的印象,而利用这样的材料可以制成光敏电阻,利用这点作用可以方便的设计光控电路以及光的测量和光电转换等领域。
材料电阻率测试仪厂家直销 参数
测量参数 绝缘电阻R,泄漏电流I,表面电阻Rs,体积电阻Rv
测试电压1-1000v 1000个档位可以调
测试范围 电阻5*102Ω~1*1016Ω(超出显示电流最大换算可到20次方), 电阻率最高可达到1022Ω.cm
测量方式:手动/自动两种
界面语言选择:英文/中文 两种
显示位数:4/5位 两种选择
测量模式:三种
测试速度可选择 快速5次/秒,慢速1次/秒,两种可选
回读电压精度 0.5%?1V
测试特点:带设置记忆功能开机一键测试出结果不用反复设置
可设定测量延时和放电延时
十种自定义测量模式可以用户自己编辑开机直接调取满足不同材料的测试需求
量程超限显示 量程上超
输入端子 香蕉插头,BNC插头
精度保证期 1年 根据计量证书有效期 可在全国任意检测所检测精度保证
操作温度和湿度0℃到40℃80%RH以下(无凝结)
存储温度和湿度-10℃到60℃80%RH以下(无凝结)
操作环境 室内,最高海拔2000m
电源 电压:110V/ 220V AC频率:47Hz/63Hz 两种供电模式
功耗 50 W
尺寸 约331 mm x 329 mm x 80 mm
重量 约4.1kg
说明
1.电阻率ρ不仅和导体的材料有关,还和导体的温度有关。在温度变化不大的范围内:几乎所有金属的电阻率随温度作线性变化,即ρ=ρo(1 at)。式中t是摄氏温度,ρo是O℃时的电阻率,a是电阻率温度系数。
2.由于电阻率随温度改变而改变,所以对于某些电器的电阻,必须说明它们所处的物理状态。如一个220 V -100 W电灯灯丝的电阻,通电时是484欧姆,未通电时只有40欧姆左右。

3.电阻率和电阻是两个不同的概念。电阻率是反映物质对电流阻碍作用的属性,电阻是反映物体对电流阻碍作用的能力大小。
4.超导体的直流电阻率在一定的低温下突然消失,被称作零电阻效应。导体没有了电阻。
金属的电阻率较小,合金的电阻率较大,非金属和一些金属氧化物更大,而绝缘体的电阻率极大。锗、硅、硒、氧化铜、硼等的电阻率比绝缘体小而比金属大,我们把这类材料叫做半导体(semiconductors)。
总结:常态下(由表可知)导电性能好的依次是银、铜、铝,这三种材料是常用的,常被用来作为导线等。银的价格偏贵,因此铜用的为广,几乎所有应用的导线都是铜制作的(精密仪器、特殊场合除外)。铝线由于化学性质不稳定容易氧化已被淘汰。由于铝密度小,取材广泛,且价格比铜便宜,被广泛用于电力系统中传输电力的架空输电线路。为解决铝材刚性不足缺陷,一般采用钢芯铝绞线,即铝绞线内部包有一根钢线,以提高强度。银导电性能好,但由于成本高很少被采用,只有在高要求场合才被使用,如精密仪器、高频震荡器、航天等。在某些场合仪器上触点也有用金的,因为金的化学性质稳定,并不是因为其电阻率小所致。
The function of resistance:
The role of resistance in circuits: Using the famous Ohm's law, resistance can be used to control the voltage and current in a circuit.
The main physical characteristic of resistance is that it can convert electrical energy into thermal energy, so the heating elements, light bulbs, and electric irons in water heaters are made using the effect of resistance. In addition, resistors have the characteristic of being sensitive to heat. When the temperature of the conductor material increases, the resistivity of the material will increase (some materials show a decrease). Therefore, using this characteristic of resistors can be used to make temperature measuring instruments (I don't know if you have seen it, the method of measuring temperature by inserting a "wire" is based on the effect of this resistor material).
In addition, the resistance of some materials can also be affected by light exposure, and using such materials can make photoresistors. This can facilitate the design of light control circuits, as well as the measurement and photoelectric conversion of light.
parameter
Measurement parameters include insulation resistance R, leakage current I, surface resistance Rs, and volume resistance Rv
Test voltage 1-1000v, adjustable in 1000 gears
The test range of resistance is 5 * 102 Ω~1 * 10 16 Ω (beyond the maximum displayed current, it can be converted to the power of 20), and the highest resistivity can reach 1022 Ω. cm
Measurement methods: manual/automatic
Interface language selection: English/Chinese
Display digits: 4/5 digits with two options
Measurement modes: three types
The testing speed can be selected as fast 5 times/second or slow 1 time/second, two options are available
Readback voltage accuracy 0.5% ? 1V
Test feature: Equipped with setting memory function, one click power on test results can be obtained without repeated settings
Measurement delay and discharge delay can be set
Ten custom measurement modes can be edited by users themselves, and can be directly accessed upon startup to meet the testing needs of different materials
Range Exceeding Display Range Exceeding Range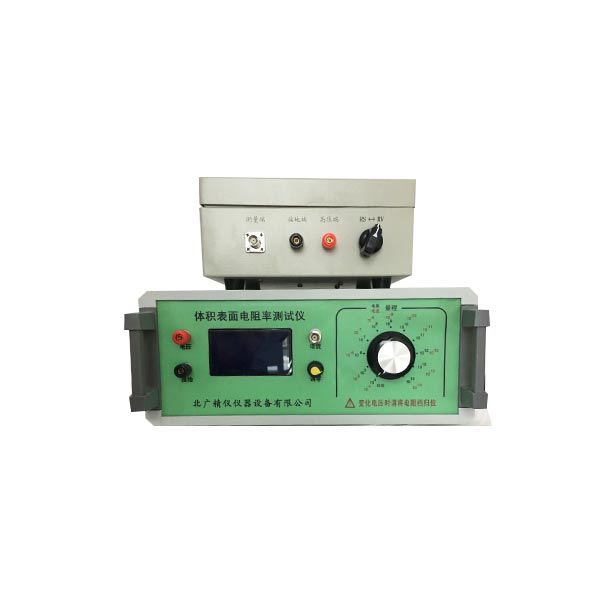

Input terminal banana plug, BNC plug
The accuracy guarantee period is 1 year. According to the validity period of the measurement certificate, the accuracy guarantee can be tested at any testing center nationwide
Operating temperature and humidity: 0 ℃ to 40 ℃, below 80% RH (no condensation)
Storage temperature and humidity -10 ℃ to 60 ℃ below 80% RH (no condensation)
Operating environment indoors, with a maximum altitude of 2000m
Power supply voltage: 110V/220V AC frequency: 47Hz/63Hz two power supply modes
Power consumption 50 W
Size approximately 331 mm x 329 mm x 80 mm
Weight approximately 4.1kg
describe
The resistivity ρ is not only related to the material of the conductor, but also to the temperature of the conductor. In the range where temperature changes little: the resistivity of almost all metals varies linearly with temperature, that is, ρ=ρ o (1 at). In the formula, t is the temperature in Celsius, ρ o is the resistivity at O ℃, and a is the temperature coefficient of resistivity.
2. As the resistivity changes with temperature, it is necessary to explain the physical state of the resistance of certain electrical appliances. The resistance of a 220 V -100 W electric lamp filament is 484 ohms when powered and only about 40 ohms when not powered.
3. Electrical resistivity and resistance are two different concepts. Electrical resistivity is a property that reflects the obstruction of current by a substance, and resistance is the ability of an object to obstruct current.
The sudden disappearance of the DC resistivity of superconductors at a certain low temperature is called the zero resistance effect. The conductor has lost its resistance.
The electrical resistivity of metals is relatively low, that of alloys is relatively high, that of non metals and some metal oxides is even higher, and that of insulators is extremely high. Germanium, silicon, selenium, copper oxide, boron, and other materials have lower electrical resistivity than insulators but higher resistivity than metals. We call these materials semiconductors.
Summary: Under normal conditions (as shown in the table), silver, copper, and aluminum have good conductivity, and these three materials are commonly used as wires. Silver is relatively expensive, so copper is widely used, and almost all wires used in applications are made of copper (except for precision instruments and special occasions). Aluminum wire has been phased out due to its unstable chemical properties and easy oxidation. Due to its low density, wide availability, and lower price compared to copper, aluminum is widely used in overhead transmission lines for power transmission in the power system. To solve the problem of insufficient rigidity of aluminum materials, steel core aluminum stranded wire is generally used, which is wrapped with a steel wire inside the aluminum stranded wire to improve its strength. Silver has good conductivity, but it is rarely used due to its high cost and is only used in high demand applications such as precision instruments, high-frequency oscillators, aerospace, etc. In some occasions, gold is also used as a contact on instruments because its chemical properties are stable and not due to its low electrical resistivity.
影响电阻率的外界因素
电阻率不仅与材料种类有关,而且还与温度、压力和磁场等外界因素有关。金属材料在温度不高时,ρ与温度t(℃)的关系是ρt=ρ0(1 at),式中ρt与ρ0分别是t℃和0℃时的电阻率;α是电阻率的温度系数,与材料有关。锰铜的α约为1?10-1/℃(其数值极小),用其制成的电阻器的电阻值在常温范围下随温度变化极小,适合于作标准电阻。已知材料的ρ值随温度而变化的规律后,可制成电阻式温度计来测量温度。半导体材料的α一般是负值且有较大的量值。制成的电阻式温度计具有较高的灵敏度。有些金属(如Nb和Pb)或它们的化合物,当温度降到几K或十几K(绝对温度)时,ρ突然减少到接近零,出现超导现象,超导材料有广泛的应用前景。利用材料的ρ随磁场或所受应力而改变的性质,可制成磁敏电阻或电阻应变片,分别被用来测量磁场或物体所受到的机械应力,在工程上获得广泛应用。
什么是电阻率:
电阻率是用来表示各种物质电阻特性的物理量。某种物质所制成的原件(常温下20?C)的电阻与横截面积的乘积与长度的比值叫做这种物质的电阻率。电阻率与导体的长度、横截面积等因素无关,是导体材料本身的电学性质,由导体的材料决定,且与温度、压力、磁场等外界因素有关。
电阻率在国际单位制中的单位是Ω?m,读作欧姆米,简称欧米。常用单位为“欧姆?厘米”。
微分电阻
如电阻跟随电压及电流变动,则可定义微分电阻为:
dU
r=--
dI
微分电阻的单位仍为欧姆,惟微分电阻值与基本的电阻值并不一致。微分电阻值有可能因有关仪器的特性而出现负值,称为负电阻。然而,基本电阻(即电压与电流的商)永远为正值。
为什么测量时仪器的读数总是不稳?
一般的材料其导电性不是严格像标准电阻样在一定的电压下有很稳定的电流,有很多材料特别是防静电材料其导电性不符合欧姆定律,所以在测量时其读数不稳。
这不是仪器的问题,而是被测量物体的性能决定的。有的标准规定以测量1分钟时间的读数为准。通常在测量高电阻或微电流时测量准确度因重复性不好,对测量读数只要求2位或3位。另外在测量大电阻时如果屏蔽不好也会因外界的电磁信号对仪器测量结果造成读数不稳。
External factors affecting resistivity
The resistivity is not only related to the type of material, but also to external factors such as temperature, pressure, and magnetic field. When the temperature of a metal material is not high, the relationship between ρ and temperature t (℃) is ρ t=ρ 0 (1 at), where ρ t and ρ 0 are the resistivity at t ℃ and 0 ℃, respectively; α is the temperature coefficient of resistivity, which is related to the material. The alpha value of manganese copper is about 1 ? 10-1/℃ (its value is extremely small), and the resistance value of resistors made from it changes very little with temperature in the normal temperature range, making them suitable for use as standard resistors. After knowing the law of the variation of the material's ρ value with temperature, a resistance thermometer can be made to measure temperature. The alpha value of semiconductor materials is generally negative and has a large magnitude. The resistance thermometer made has high sensitivity. Some metals (such as Nb and Pb) or their compounds, when the temperature drops to a few K or tens of K (absolute temperature), suddenly decrease in ρ to near zero, resulting in superconductivity. Superconducting materials have broad application prospects. By utilizing the property of the material's ρ changing with magnetic field or stress, magnetic sensitive resistors or resistance strain gauges can be made, which are used to measure the mechanical stress of magnetic fields or objects, and have been widely used in engineering.
What is electrical resistivity:
Electrical resistivity is a physical quantity used to represent the resistance characteristics of various substances. The ratio of the product of the electrical resistance and cross-sectional area to the length of a component made of a certain substance (at 20 ? C at room temperature) is called the electrical resistivity of the substance. The resistivity is independent of factors such as the length and cross-sectional area of the conductor, and is the electrical property of the conductor material itself. It is determined by the material of the conductor and is related to external factors such as temperature, pressure, and magnetic field.
The unit of electrical resistivity in the International System of Units is Ω? m, pronounced as ohm meter, abbreviated as ohm meter. The commonly used unit is "ohm ? centimeter".
differential resistance
If the resistance follows the changes of voltage and current, the differential resistance can be defined as:
dU
r=--
dI
The unit of differential resistance is still ohms, but the value of differential resistance is not consistent with the basic resistance value. The differential resistance value may have negative values due to the characteristics of the instrument, which is called negative resistance. However, the fundamental resistance (i.e. the quotient of voltage and current) is always positive.
Why is the reading of the instrument always unstable during measurement?
The conductivity of general materials is not as strict as that of standard resistors, which have a stable current at a certain voltage. Many materials, especially anti-static materials, have conductivity that does not comply with Ohm's law, so their readings are unstable during measurement.
This is not a problem with the instrument, but rather determined by the performance of the object being measured. Some standards stipulate that the reading should be based on measuring 1 minute of time. Usually, when measuring high resistance or microcurrents, the measurement accuracy is poor due to poor repeatability, and only 2 or 3 digits are required for the measurement reading. In addition, if the shielding is not good when measuring high resistance, the measurement results of the instrument may be unstable due to external electromagnetic signals.
体积表面电阻率测试仪是一种用于测量材料绝缘性能的精密仪器,广泛应用于多个行业,主要涉及对材料电绝缘性能有严格要求的领域。北京北广精仪仪器设备有限公司声场的体积表面电阻率测试仪主要用于以下主要适用行业及具体应用场景:
1. 电子与半导体行业
应用:测试PCB基板、绝缘薄膜、封装材料、半导体晶圆等的电阻率,确保其绝缘性能满足电子元件防短路、防漏电的要求。
案例:评估手机电路板在高湿度环境下的绝缘可靠性。
2. 电力与能源行业
应用:检测电缆绝缘层、变压器油、复合绝缘子等材料的电阻率,保障高压设备的安全运行。
案例:高压电缆出厂前的绝缘性能验证。
3. 航空航天与汽车制造
应用:评估飞机复合材料、汽车线束、电池隔膜等材料的电绝缘性,防止静电积聚或电磁干扰。
案例:新能源汽车电池组绝缘材料的质量控制。
4. 科研与新材料开发
应用:研究石墨烯、纳米涂层等新型材料的导电/绝缘特性,优化材料配方。
案例:柔性显示技术中透明导电薄膜的研发测试。
5. 医疗设备与生物材料
应用:检测医用塑料、导管、植入材料的绝缘性能,确保患者安全。
案例:心脏起搏器绝缘外壳的生物兼容性测试。
6. 塑料与橡胶工业
应用:质量控制环节中测量工程塑料、硅橡胶等材料的电阻率,用于防静电包装或绝缘部件生产。
案例:防静电托盘用于芯片运输前的电阻率达标测试。
6. 军事与国防
应用:评估隐身涂层、雷达吸波材料等的电学性能。
7 案例:军用无人机复合材料的电磁屏蔽效能测试。
8. 建材与家居行业
应用:检测地板、墙板的防静电性能(如数据中心地板)或绝缘性能(如电工套管)。
案例:洁净室防静电地板的验收测试。
9.能源存储(电池与电容器)
应用:测量隔膜、电解质的电阻率,优化锂电池或超级电容器的性能。
案例:锂电隔膜孔隙率对离子传导性的影响研究。
10. 质量控制与认证机构
应用:作为第三方检测工具,依据ISO/ASTM标准对材料进行认证(如UL认证、RoHS合规性)。
案例:出口电子产品的绝缘安全认证测试。
关键测试参数
体积电阻率(Ω?cm):反映材料内部的绝缘性能。
表面电阻率(Ω/sq):评估材料表面的导电/防静电特性。
行业标准参考
测试常遵循国际标准如IEC 60093、ASTM D257、GB/T 1410等,确保数据可比性。
总之,该仪器是材料电学性能评估的核心设备,覆盖从基础研究到工业生产的全链条需求,尤其在需要高可靠性绝缘或可控导电性的场景中不可或缺。
业务咨询:932174181 媒体合作:2279387437 24小时服务热线:15136468001 盘古机械网 - 全面、科学的机械行业免费发布信息网站 Copyright 2017 PGJXO.COM 豫ICP备12019803号