电容器纸绝缘电阻测试仪 保护:测量仪器用的绝缘材料一般只具有与被测材料差不多的性能.试样的测试误差可以由下列原因产生:
①外来寄生电压引起的杂散电流通渠道.通常不知道它的大小,并且有漂移的特点;
②测量线路的绝缘材料与试样电阻标准电阻器或电流测量装置的并联.
使用高电阻绝缘奢侈可以改善测量误差,但这种方法将使仪器昂贵而又笨重,而且对高阻值试样的测量仍不能得到满意的结果.较为满意的改进方法是使用保护技术,即在所有主要的绝缘部位安置保护导体,通过它截信了各种可能引起误差的杂散电流;将这些导电联接在一起组成保护系统,并与测量端形成一个三端网络.当线路连接恰当时,所有外来寄生电压的杂散电流被子保护系统分流到测量电路以下,这就可大大减少误差的可能性.
电容器纸绝缘电阻测试仪 在系统的保护端和被保护端之间存在的电解电势,接触电势或热电运势较小时,均能补偿掉,使它们在测量中不引起显著误差.
在电流测量中,由于被保护端和保护端之间的电阻与电流测量装置并联可能产生误差,因此前者至少应为电流测量装置输入电阻的10倍,最好为100倍.在电桥法测量中,保护端与测量端带有大致相同的电位,但电桥中的一个标准电阻与不保护端和保护端之间的电阻并联,因此,后者至少为标准电阻的10倍,最好20倍.
在开始测试前先断开电源和试样的连线进行一次测量,此时设备应在它的灵敏度许可范围内指示无穷大的电阻.可用一些已知值的标准电阻业检查设备运行是否良好.
表面电阻率surface resistivity
在绝缘材料的表面层里的直流电场强度与线电流密度之商,即单位面积内的表面电阻。面积的大
小是不重要的。
注:表 面 电 阻 率 的S1单 位 是Q。实 际 上 有 时 也 用 “欧 每 平 方 单 位 ”来 表 示 。
标准:GB/T 1410-2006《 塑料薄膜电阻率测定仪固体绝缘材料体积电阻率和表面电阻率试验方法》
GB/T 1410-2006本标准规定了固体绝缘材料体积电阻率和表面电阻率的试验方法。这些试验方法包括对固体绝缘材料体积电阻和表面电阻的测定程序及体积电阻率和表面电阻率的计算方法
体积电阻和表面电阻的试验都受到下列因素影响:施加电压的大小和时间;电极的性质和尺寸;在
试样处理和测试过程中周围大气条件和试样的温度、湿度。
技术指标
1、电阻测量范围:0.01?104Ω~1?1018Ω。
2、电流测量范围:2?10-4A~1?10-16A
3、显示方式:触摸屏、电阻、电阻率、电流、电压。
4、内置测试电压:10V、50V、100V、250V、500V、1000V(任意切换)
5、基本准确度:1%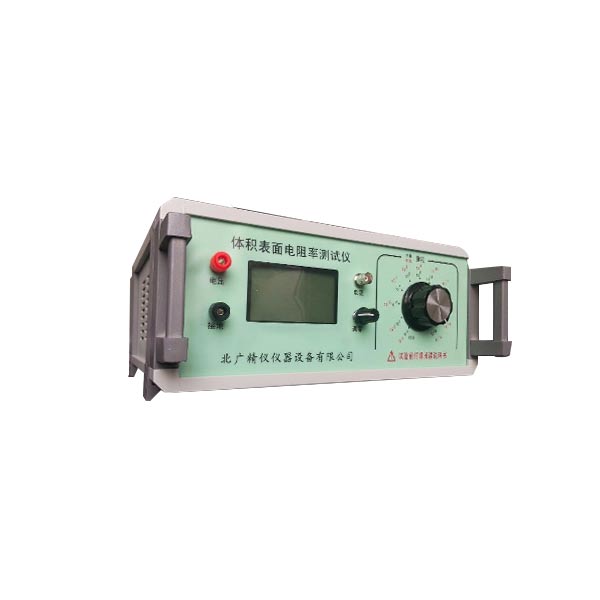
6、使用环境:温度:0℃~40℃,相对湿度<80%
7、供电形式:AC220V,50HZ,功耗约5W
8、仪器尺寸:360*350*170mm
9、质量:主机约5KG
影响电阻率的外界因素
电阻率不仅与材料种类有关,而且还与温度、压力和磁场等外界因素有关。金属材料在温度不高时,ρ与温度t(℃)的关系是ρt=ρ0(1 at),式中ρt与ρ0分别是t℃和0℃时的电阻率;α是电阻率的温度系数,与材料有关。锰铜的α约为1?10-1/℃(其数值极小),用其制成的电阻器的电阻值在常温范围下随温度变化极小,适合于作标准电阻。已知材料的ρ值随温度而变化的规律后,可制成电阻式温度计来测量温度。半导体材料的α一般是负值且有较大的量值。制成的电阻式温度计具有较高的灵敏度。有些金属(如Nb和Pb)或它们的化合物,当温度降到几K或十几K(绝对温度)时,ρ突然减少到接近零,出现超导现象,超导材料有广泛的应用前景。利用材料的ρ随磁场或所受应力而改变的性质,可制成磁敏电阻或电阻应变片,分别被用来测量磁场或物体所受到的机械应力,在工程上获得广泛应用。
电阻的作用:
电阻在电路中的作用:利用著名的欧姆定律可以利用电阻控制电路中的电压、电流。
电阻的主要物理特征就是可以变电能为热能,因此热水器中的发热元件、电灯泡、电烫斗就是利用了电阻的作用制成的。另外电阻有怕热的特性,当导体材料温度升高时材料的电阻率会增大(有些材料则表现为减小),因此利用电阻的这种特性可以制作温度测量计(不知道你看见过没,插一根“铁丝”就能测量温度的方法就是利用了这种电阻材料作用的)。
另外一些材料的电阻还会受到光线照射的印象,而利用这样的材料可以制成光敏电阻,利用这点作用可以方便的设计光控电路以及光的测量和光电转换等领域。
安全注意事项
1.使用前务必详阅此说明书,并遵照指示步骤,依次操作。
2.请勿使用非原厂提供之附件,以免发生危险。
3.进行测试时,本仪器测量端高压输出端上有直流高压输出,严禁人体接触 ,以
免触电。
4.为避免测试棒本身绝缘泄漏造成误差,接仪器测量端输入的测试棒应尽可 能悬
空,不与外界物体相碰。
5. 当被测物绝缘电阻值高,且测量出现指针不稳现象时,可将仪器测量线屏蔽端夹子接上。例如:对电缆测缆芯与缆壳的绝缘时,除将被测物两端分别接于输入端与高压端,再将电缆壳,芯之间的内层绝缘物接仪器“G”,以消 除因 表面漏 电而 引起的测 量误 差。也 可用 加屏蔽 盒的 方法, 即将 被测物 置于 金属屏 蔽盒 内,接 上测 量线。
Safety precautions
1. Be sure to read this manual carefully before use, and operate in sequence according to the instructions.
2. Do not use accessories not provided by the original manufacturer to avoid danger.
3. During the test, there is a DC high-voltage output on the high-voltage output end of the measuring end of the instrument. It is strictly forbidden to touch the human body
No electric shock.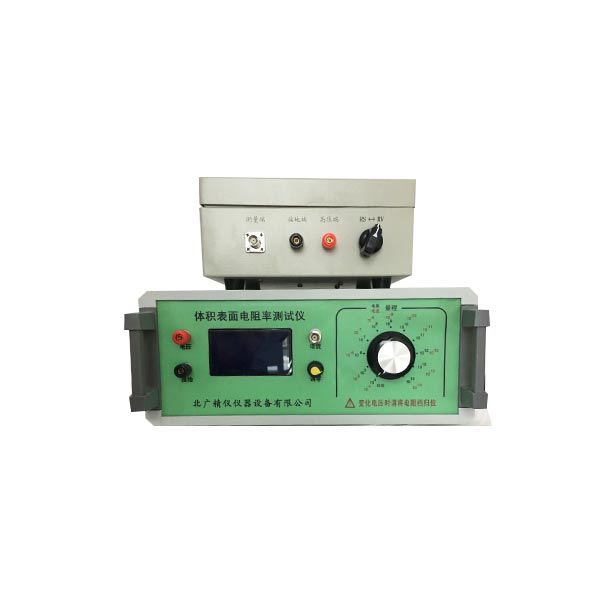
4. In order to avoid errors caused by insulation leakage of the test bar itself, the test bar connected to the measuring end of the instrument shall be suspended as much as possible
It is empty and does not collide with external objects.
6. When the insulation resistance of the measured object is high and the pointer is unstable during measurement, connect the clamp at the shielding end of the measuring line of the instrument. For example, when measuring the insulation between the cable core and the cable shell, in addition to connecting the two ends of the measured object to the input end and the high-voltage end, connect the inner insulation between the cable shell and the core to the instrument "G" to eliminate the measurement error caused by surface leakage. The method of adding a shielding box can also be used, that is, placing the tested object in a metal shielding box and connecting the measuring line.
测试步骤:
1、测试温度23?2℃,相对湿度65?5%,无外界电磁场干扰环境中进行。
2、测试时对试样所加电压为100V~500V的直流电压,选择电压档次。
3、将试样倒入高压电极内,使液面刚好和环电极下缘全部接触为止。
4、将充分放电后的试样和电极,按固体(液体)体积及表面电阻率测试仪要求接线。
外电极(高压电极)接高固体(液体)体积及表面电阻率测试仪的高压输出端。
内电极(测量电极)接固体(液体)体积及表面电阻率测试仪的测量端。
中电极(环电极)接固体(液体)体积及表面电阻率测试仪的接地端。
5、仪器预热30分钟,稳定后调整仪器(调零),加上试验1分钟,读取电阻指示值,然后放电1分钟,再测试一次,以二次的算术平均值作为试验样品电阻指示值。
表面电阻率 沿试样表面电流方向的直流电场强度与单位长度的表面传导电流之比,称材料的表面电阻率,以符号ρm表示。板状试样的表面电阻率可按下式计算:
ρm=Rm[2π?ln(d2?d1)]
式中Rm—试样表面电阻,即施加在试样上的直流 电压与电极间表面传导电流之比(Ω);
d1—平板测量电极直径(m);
d2—平板保护电极内径(m),

Importance and use:
1 The insulating material is used to isolate the electronic systems from each other and from the ground. It can provide mechanical support for parts. For this purpose, the highest possible insulation resistance is usually required to be consistent with acceptable mechanical, chemical and heat resistance. Because the insulation resistance or conductance combines the volume and surface resistance or conductance, the test sample and electrode are required to have the same form in actual use, and the measured value at this time is very useful. The surface resistance or conductance changes rapidly with humidity, while the volume resistance or conductance changes slightly, although the overall change may be greater in some cases.
2 Resistance or conductance can be used to indirectly predict the low frequency dielectric breakdown and loss factor performance of some materials. Resistance or conductance is usually used as an indirect measure of humidity content, curing degree, mechanical continuity or different types of aging. The utility of these indirect measures depends on the degree of correlation established through theoretical or empirical research. The reduction of surface resistance can lead to the increase of dielectric breakdown voltage due to the reduction of electric field strength, or the decrease of dielectric breakdown voltage due to the increase of stress area.
3 All dielectric resistances or conductivities depend on the length of the electrochemical time and the applied voltage (except for ordinary environmental variables). These factors must be known and reported at the same time to make resistance or conductance measurements meaningful. In the electrical insulating material industry, the adjective "apparent" is usually applicable to the resistance value obtained under the condition of arbitrarily choosing the electrochemical time. See X1.4.
4 The volume resistance or conductance can be calculated from the resistance and size data used to design an insulator for a specific application. Studies have shown that resistance or conductance varies with temperature and humidity (1,2,3,4) 4, and this change must be known when designing operating conditions. The volume resistance or conductance measurement value is usually used to check the uniformity of insulating materials, or for processing, it can detect conductive impurities that affect the quality of materials, which is not easily observed by other methods.
5 When the volume resistance exceeds 1021Ω?cm (1019Ω?cm), the volume resistance is calculated from the value obtained from the test of the sample under ordinary laboratory conditions. If the result is really suspicious, the limitations of the commonly used measuring equipment should be considered.
6 The surface resistance or conductance cannot be measured accurately, but can only be measured approximately, because the volume resistance or conductance is always affected by the measurement method. The measured values are also affected by surface contamination. Surface contamination and its accumulation rate are affected by many factors, including electrostatic charging and interfacial tension. These factors in turn can affect surface resistance. When pollution is included, but the material properties that are not electrical insulating materials are judged under common sense, the surface resistance or conductance can be regarded as related to the material properties.
业务咨询:932174181 媒体合作:2279387437 24小时服务热线:15136468001 盘古机械网 - 全面、科学的机械行业免费发布信息网站 Copyright 2017 PGJXO.COM 豫ICP备12019803号